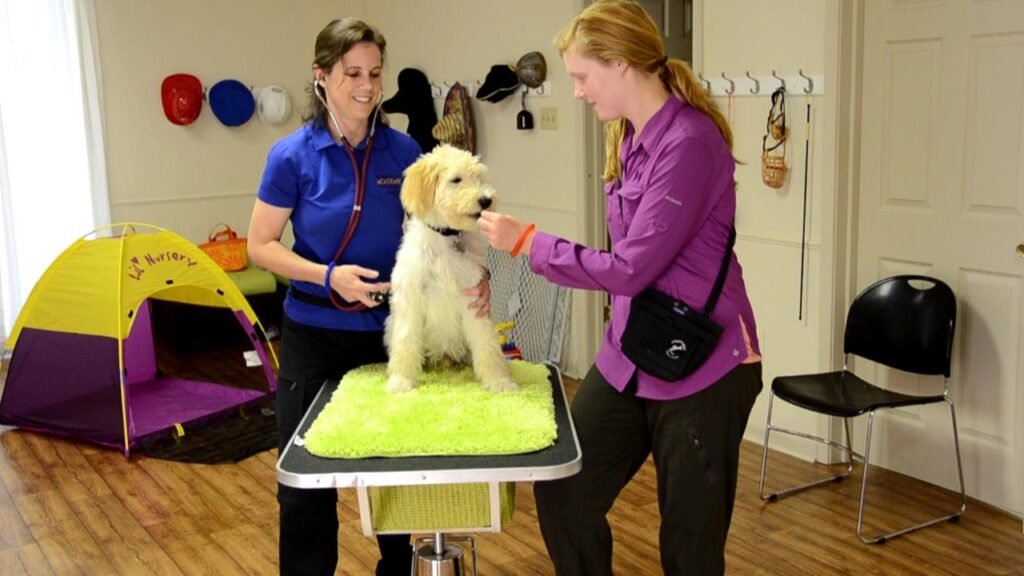

In research published in Journal of the American Veterinary Medical Association in November, 32 dogs underwent a standardized exam consisting of examination of the head, palpation of lymph nodes and body, axillary temperature measurement, heart rate assessment, and respiratory rate assessment. The exams were recorded on video under two conditions, with owners present or absent. Behaviors indicating fear were assessed, including reduced posture, avoidance, escape, lip licking, body shaking, yawning, and vocalizing; physiological measures were also taken.
Based on their findings, researchers concluded dogs were less stressed when the owner was present during the exam.
“When the owners were allowed to be present with their dogs, they did have more reduced fear levels: reduced vocalizations and reduced temperature, and we also saw some female dogs had lower heart rates when they were with their owners,” says coauthor Anastasia C. Stellato. “So our results show that, if possible and if it’s appropriate for that client, to allow owners to be in the exam room could have a beneficial impact.”
Owner presence didn’t eliminate fear: more extreme responses, such as attempting to escape, were the same in both groups, despite the superficial nature of the exam. “It’s important to keep in mind that the exam we conducted was very passive,” says Stellato. “It was on the ground, they had a traction mat, we didn’t even use rectal temperature, and yet we still saw those fearful responses.”
So while those reactions indicated that the dogs would have preferred to avoid the exam, owner presence apparently allowed them to tolerate it somewhat better.
The study found an age difference in that older dogs lip-licked less than younger dogs when their owner was present. It’s possible that this was the result of a stronger bond developed over the years, but since length of ownership was not recorded, this remains a hypothesis for further investigation.
One finding that was surprising to the researchers was that owner-present dogs yawned more. Yawning is a complex behavior in dogs, so this result is difficult to interpret. “It was contrary to our expectation, so it requires further investigation,” says Stellato.
On the whole, the results suggest that when possible, allowing the owner to be present can be a simple way to reduce stress.
Veterinary behaviorist Karen van Haaften, senior manager of behaviour and welfare at British Columbia SPCA, says: “I think it’s a nicely designed study. It’s randomized and controlled, which is nice to see in a clinical study. I personally am not surprised by the results of this paper, but I think it’s really useful information for both veterinarians and pet owners to know, and I think it’s a timely one to consider, because during COVID, most vets are not allowing pet owners into the hospital.”
Even after the pandemic is over, pets will still need to be separated from their owners sometimes, so ways to mitigate the stress of this experience need to be considered. Van Haaften says: “When I read this, I’m asking myself, why are we seeing this response? Is it the social support — the bond that the pet has with the owner — that is reassuring to them? Or is the lack of familiarity? They don’t see anything in this clinic environment that feels familiar to them. Probably it’s both, but if the second, we can work on that.”
When pets do need to be separated from their owner, she says, consider how to include things familiar to the pet in the experience.
“We can interact with them in the way that we see that the owner does – use cues the owner uses, use training that they already know, walk them in on equipment that’s familiar, maybe bring something familiar from the owner into the room with them.”
Post-pandemic, we can return to the idea that familiarizing pets with the clinic in advance; for instance, dropping in simply to get some treats and meet friendly people. “If you do that a couple times a week they’re going to love going into the clinic — now it’s a familiar place where good things happen to them.”
And in some cases, a very little bit of familiarization right before an exam can make a big difference. “For some dogs, it doesn’t take that long to bond with a person,” van Haaften says. “If a technician or someone spends five minutes feeding cookies, performing trained cues with a dog, suddenly, now they’re good friends, and the dog has a familiar person they can go into the clinic with.”
Some clinics are doing exams outdoors for pets who are stressed inside the clinic, which can allow the owner to be nearby and this might be worth continuing for some pets as well. In general, van Haaften recommends flexibility and attention to individual differences.
“Behavior during vet exams is really complicated, and different techniques are going to work with different animals,” she says. “Be creative, be willing to be flexible about how you do exams to give your patients the best experience.”
This article was reviewed/edited by board-certified veterinary behaviorist Dr. Kenneth Martin and/or veterinary technician specialist in behavior Debbie Martin, LVT.


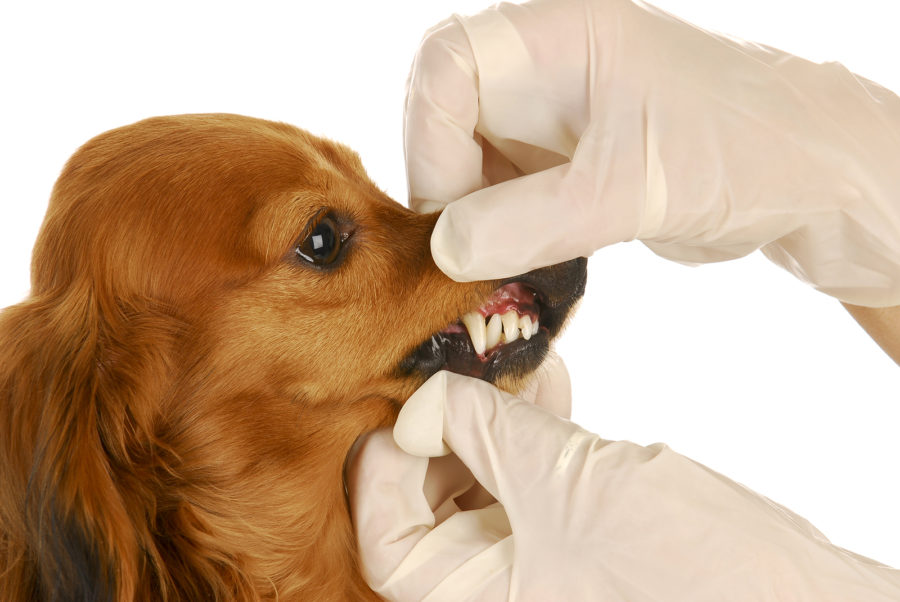
 the mucosa, and the inner surfaces of the lips. Because it’s so painful, a dog may have difficulty eating and be reluctant to open the mouth. This can result in weight loss. Other typical signs include fetid breath, thick, ropey saliva, blood-tinged saliva, visible irritability, depression and lethargy, and pawing at the mouth.
the mucosa, and the inner surfaces of the lips. Because it’s so painful, a dog may have difficulty eating and be reluctant to open the mouth. This can result in weight loss. Other typical signs include fetid breath, thick, ropey saliva, blood-tinged saliva, visible irritability, depression and lethargy, and pawing at the mouth.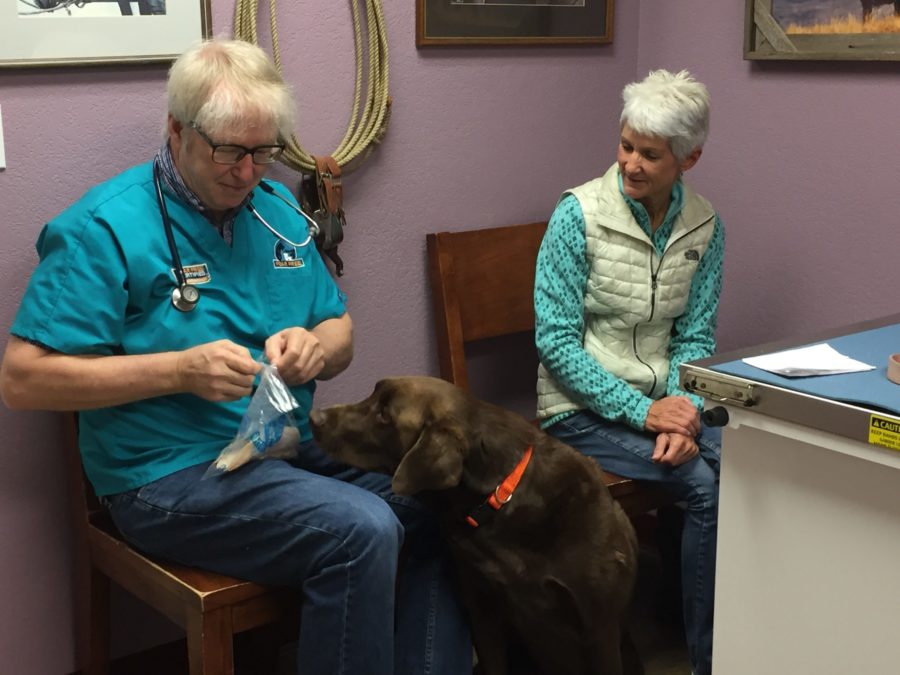






 Here’s a good rule of thumb when choosing a chew toy: if you can’t easily bend it with your hands or if you wouldn’t want to be hit in the knee with it, don’t give it to a pet. Wild dogs and wolves often have multiple fractures in their mouths due to chewing on bones.
Here’s a good rule of thumb when choosing a chew toy: if you can’t easily bend it with your hands or if you wouldn’t want to be hit in the knee with it, don’t give it to a pet. Wild dogs and wolves often have multiple fractures in their mouths due to chewing on bones.