Managing pain and completing procedures and exams in a way that keeps patients not only calm but actually eager—or at least willing—to participate is at the heart of Fear Free. We love hearing how Fear Free techniques help your patients and your own pets make it through needle sticks, diagnostic tests, and more to receive the care they need in a kind, respectful, and stress-less way both in the clinic and at home.
Fluid Dynamics
 My cat Cleo is nearly 17 and receives sub-q fluids regularly at home. She used to grumble and try to get away but once I started Fear Free, I began giving her favorite crunchy treats before, during, and after administering fluids. Now she purrs through the whole procedure, and any time I approach the spot in the house where we do fluids, she walks up for “crunchie time.” I’ve been able to switch back to a larger needle because she doesn’t notice the poke while snacking, which makes administration faster, too.
My cat Cleo is nearly 17 and receives sub-q fluids regularly at home. She used to grumble and try to get away but once I started Fear Free, I began giving her favorite crunchy treats before, during, and after administering fluids. Now she purrs through the whole procedure, and any time I approach the spot in the house where we do fluids, she walks up for “crunchie time.” I’ve been able to switch back to a larger needle because she doesn’t notice the poke while snacking, which makes administration faster, too.
Kate Regehr, Douglas College, New Westminster, British Columbia, Canada
PVPs for Moose
Last year, Moose came into our clinic with lots of anxiety and fear, so much that we were unable to properly perform a physical exam or collect blood from him. This year, Moose had trazodone on board and his visit went fantastic. Our team was able to get him on the scale, perform a full exam, and collect blood. Moose’s mom was so happy and relieved to know that Moose could have a Fear Free veterinary visit where Moose can feel safe.
Jessica Decock, Georgian Bay Veterinary Hospital and Mobile Services, Perkinsfield, Ontario, Canada
Pain Relief, Pet Relief
 Chewy had a lot of fear and anxiety at the veterinary clinic, causing her to behave aggressively and making it difficult to give her the care she needed. While training her, I observed various signs of pain, which were most likely adding to her anxiety. I alerted her caregiver to my observations so she could better assess and monitor her dog and update her veterinarian. Chewy and her caregiver had previously had negative and traumatic experiences at a veterinary clinic so I referred them to Keystone Veterinary Clinic, which has Fear Free Certified Professionals who created a handling plan to enable Chewy to have a thorough exam, radiographs, and other diagnostics in a safe and low-stress manner. I also worked with the owner to begin muzzle training. The combination of appropriate scheduling, handling, and sedation, Chewy was able to receive the diagnostics and treatment she needed.
Chewy had a lot of fear and anxiety at the veterinary clinic, causing her to behave aggressively and making it difficult to give her the care she needed. While training her, I observed various signs of pain, which were most likely adding to her anxiety. I alerted her caregiver to my observations so she could better assess and monitor her dog and update her veterinarian. Chewy and her caregiver had previously had negative and traumatic experiences at a veterinary clinic so I referred them to Keystone Veterinary Clinic, which has Fear Free Certified Professionals who created a handling plan to enable Chewy to have a thorough exam, radiographs, and other diagnostics in a safe and low-stress manner. I also worked with the owner to begin muzzle training. The combination of appropriate scheduling, handling, and sedation, Chewy was able to receive the diagnostics and treatment she needed.
Tabitha Kucera, RVT, CCBC, KPA-CTP, Positively Pawsitive, Cleveland, Ohio
Meeting Goals for Gus
 Gus had developed severe resource guarding of his food and water bowls, as well as fear and anxiety regarding being touched and having his gear put on and taken off. As a result, he snapped at and bit a walker. We worked closely with his owners and utilized Fear Free strategies and positive reinforcement training to get Gus comfortable with having strangers in the home. We were eventually able to find a solution that allowed Gus to be comfortable having walkers touch and refill his water bowl and approach his food bowl without any signs of resource guarding or fear, anxiety, and stress. Now Gus happily greets his walker at the door, demands affection, and has no issues on his walk or in his home.
Gus had developed severe resource guarding of his food and water bowls, as well as fear and anxiety regarding being touched and having his gear put on and taken off. As a result, he snapped at and bit a walker. We worked closely with his owners and utilized Fear Free strategies and positive reinforcement training to get Gus comfortable with having strangers in the home. We were eventually able to find a solution that allowed Gus to be comfortable having walkers touch and refill his water bowl and approach his food bowl without any signs of resource guarding or fear, anxiety, and stress. Now Gus happily greets his walker at the door, demands affection, and has no issues on his walk or in his home.
Katie Pape, Windy City Paws, Chicago, Illinois
Turning Around First-Visit Blues
Yesterday, we had a new client come in for a vaccine appointment for her new blue merle Corgi puppy, which she had picked up the previous day. In the lobby, the pup was quiet and at first glance appeared to be coping well, but once in the exam room, I noticed she was scared and only wanted to stay between mom’s legs. We needed to vaccinate her so she could attend the puppy kindergarten class our behaviorist runs. We were able to get an oral bordetella vaccine in her, luring with baby food. When we attempted to poke with the needle for the other vaccination, though, she cried. We tried to warm her up to us so we would be able to get the vaccination in her. She escalated in the room and turned and growled. We then decided to abort mission. We did not want to ruin her experience at the veterinarian, especially since this was her first time here and she was a baby. We prescribed gabapentin and planned to have her come in the next day, early in the morning, to give her a better experience. Luckily, mom and dad were 100 percent on board with this. They came in the next morning and our front desk staff directed them to a room right away. When we walked in with the vaccine, she was asleep on the table. Dad said she was very sleepy. I grabbed a cup of Braunschweiger and fed her a small piece of it. She eagerly ate it but didn’t move her body. We desensitized and performed gradient of touch and she was fully distracted by the yummy treats. We gave her the vaccine and she never stopped eating and did not even notice the poke. We were thrilled!! Yay for pre-visit medications!
Maria Marano, The Ohio State University Veterinary Medical Center Community Practice, Columbus, Ohio





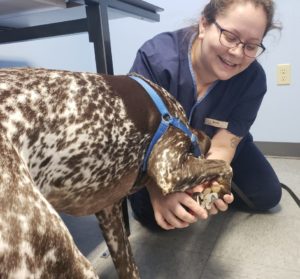 Eva, a spunky and energetic German Shorthaired Pointer, is a staff favorite for more than just her adorable, tongue-hanging-out smile, but there’s one thing Eva never liked: nail trims! Prior to the hospital’s transition to Fear Free in early 2017, it was a challenge to trim Eva’s nails, requiring three or four technicians to assist with restraint, plus a muzzle and calming cap. We started implementing Fear Free teachings right away with all of our patients, but one staff member has really gone above and beyond her commitment to Fear Free training to help Eva overcome her fear. Kayla McNeely volunteered to assist with Eva’s nail trims, and she can now perform Eva’s nail trims solo, standing, with minimal assistance from Eva’s mom, Sheila, who says, “Kayla’s patience and kindness have worked wonders with my girl.” Our hospital requires all staff members to go through Fear Free training to help ensure that all of our clients, patients, and staff have a pleasant experience during their exams. We have seen a tremendous difference in many patients at our hospital since our transition to Fear Free, but Kayla and Eva’s journey together is by far our most successful Fear Free adventure to date.
Eva, a spunky and energetic German Shorthaired Pointer, is a staff favorite for more than just her adorable, tongue-hanging-out smile, but there’s one thing Eva never liked: nail trims! Prior to the hospital’s transition to Fear Free in early 2017, it was a challenge to trim Eva’s nails, requiring three or four technicians to assist with restraint, plus a muzzle and calming cap. We started implementing Fear Free teachings right away with all of our patients, but one staff member has really gone above and beyond her commitment to Fear Free training to help Eva overcome her fear. Kayla McNeely volunteered to assist with Eva’s nail trims, and she can now perform Eva’s nail trims solo, standing, with minimal assistance from Eva’s mom, Sheila, who says, “Kayla’s patience and kindness have worked wonders with my girl.” Our hospital requires all staff members to go through Fear Free training to help ensure that all of our clients, patients, and staff have a pleasant experience during their exams. We have seen a tremendous difference in many patients at our hospital since our transition to Fear Free, but Kayla and Eva’s journey together is by far our most successful Fear Free adventure to date. One-year-old Ruba disliked having her feet touched and her nails trimmed. We trialed trazodone for six months for all nail trim visits. It started to work well, and we discovered she preferred sitting in Dr. DaCosta’s lap. Ruba now comes in for frequent nail trims with minimal restraint and no trazodone needed. We are so proud of her progress and the team’s dedication to using Fear Free techniques.
One-year-old Ruba disliked having her feet touched and her nails trimmed. We trialed trazodone for six months for all nail trim visits. It started to work well, and we discovered she preferred sitting in Dr. DaCosta’s lap. Ruba now comes in for frequent nail trims with minimal restraint and no trazodone needed. We are so proud of her progress and the team’s dedication to using Fear Free techniques. Mikey Bear used to require sedation before blood draws, but I showed his amazing humans how to hold his back leg for a blood draw and wet the vein while giving him treats to get him used to the feeling. They worked on this for a month, and when they came back, the blood draw was a snap. I discovered they had added another step to the homework and were poking the vein with a toothpick at home.
Mikey Bear used to require sedation before blood draws, but I showed his amazing humans how to hold his back leg for a blood draw and wet the vein while giving him treats to get him used to the feeling. They worked on this for a month, and when they came back, the blood draw was a snap. I discovered they had added another step to the homework and were poking the vein with a toothpick at home.
 When I worked at a veterinary emergency clinic, one of the dogs in the hospital was so fearful that he would begin to thrash and hit his head in the ground if anyone touched his leash. I sat in front of his cage with my back to him so he could become accustomed to my scent. Then I started placing treats in his cage and turning my back again. Eventually, I opened the door and put a leash on him and sat next to the door. When he came out of the cage on his own, I was able to walk him with no tension on the leash. Gaining an animal’s trust is a beautiful thing.
When I worked at a veterinary emergency clinic, one of the dogs in the hospital was so fearful that he would begin to thrash and hit his head in the ground if anyone touched his leash. I sat in front of his cage with my back to him so he could become accustomed to my scent. Then I started placing treats in his cage and turning my back again. Eventually, I opened the door and put a leash on him and sat next to the door. When he came out of the cage on his own, I was able to walk him with no tension on the leash. Gaining an animal’s trust is a beautiful thing.



